In recent years, low-carb and ketogenic diets have gained popularity for their potential health benefits, particularly in weight management and improving metabolic health. These dietary approaches involve reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat consumption. Let's delve into the key aspects, benefits, and considerations of low-carb and ketogenic diets.
Understanding Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets
Low-Carb Diet: A low-carb diet focuses on minimizing carbohydrate intake and increasing the consumption of protein and healthy fats. The specific carbohydrate threshold may vary, but typically, it involves reducing the intake of foods like grains, starchy vegetables, sugary snacks, and sweetened beverages.
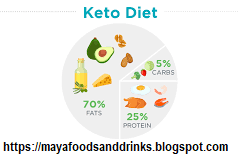
Ketogenic Diet: A ketogenic diet takes low-carb eating to the next level by significantly limiting carbohydrate intake to induce a state of ketosis. In ketosis, the body shifts its primary fuel source from carbohydrates to fats, producing ketones as an alternative energy source. This metabolic state requires careful tracking of macronutrient ratios, typically aiming for a high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate intake.
Benefits of Low-Carb and Ketogenic Diets
Weight Loss: Low-carb and ketogenic diets may support weight loss by reducing appetite, increasing satiety, and promoting fat burning due to the metabolic shift into ketosis.
Blood Sugar Control: By limiting carbohydrate intake, these diets can help stabilize blood sugar levels, making them potentially beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
Improved Lipid Profile: Some studies suggest that low-carb and ketogenic diets may improve cholesterol and triglyceride levels, contributing to better cardiovascular health markers.
Reduced Inflammation: These diets may have anti-inflammatory effects, potentially benefiting conditions associated with chronic inflammation, such as metabolic syndrome and certain autoimmune disorders.
Increased Mental Clarity: Some individuals report improved mental focus and clarity when following low-carb or ketogenic diets, although the evidence is anecdotal and may vary between individuals.
Considerations and Precautions
Potential Nutrient Deficiencies: Restricting carbohydrate-rich foods may lead to inadequate intake of certain vitamins, minerals, and fiber. Careful meal planning and diversifying food choices can help mitigate this risk.
Keto Flu: When transitioning into ketosis, some individuals experience temporary side effects, commonly known as the "keto flu." Symptoms may include fatigue, headache, dizziness, and digestive issues. Staying hydrated and ensuring sufficient electrolyte intake can help alleviate these symptoms.
Individual Variability: While low-carb and ketogenic diets can be effective for some individuals, they may not be suitable for everyone. Factors such as individual health conditions, medication use, and personal preferences should be considered. Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended before starting these diets.
Long-Term Sustainability: Adhering to a low-carb or ketogenic diet may require significant dietary changes and careful monitoring. It's important to assess whether these dietary patterns are sustainable and compatible with your lifestyle in the long run.
Conclusion
Low-carb and ketogenic diets have gained attention for their potential benefits in weight management, blood sugar control, lipid profile improvement, and reduced inflammation. However, these dietary approaches require careful consideration and individualized planning. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine the suitability and ensure nutritional adequacy when embarking on low-carb or ketogenic diets.
Top FAQs:
1. Are low-carb and ketogenic diets the same thing?
While both diets involve reducing carbohydrate intake, the ketogenic diet is a more specific and stricter form of a low-carb diet. The ketogenic diet aims to induce a state of ketosis by severely limiting carbohydrates, whereas a low-carb diet allows for a moderate reduction in carb intake without necessarily achieving ketosis.
2. Can I follow a low-carb or ketogenic diet if I'm vegetarian or vegan?
Yes, it is possible to follow a low-carb or ketogenic diet as a vegetarian or vegan. Plant-based protein sources like tofu, tempeh, seitan, nuts, and seeds can be incorporated to meet protein needs, while low-carb vegetables, healthy fats, and plant-based dairy alternatives can provide the necessary nutrients. Consulting with a registered dietitian can help tailor the diet to your specific needs.
3. Will a low-carb or ketogenic diet lead to nutrient deficiencies?
While low-carb and ketogenic diets can be nutritionally balanced, there is a risk of nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned. Certain vitamins, minerals, and fiber primarily come from carbohydrate-rich foods. Ensuring a diverse intake of non-starchy vegetables, incorporating nutrient-dense foods, and considering appropriate supplementation can help prevent nutrient deficiencies.
4. Can I exercise while on a low-carb or ketogenic diet?
Yes, exercise can be part of a low-carb or ketogenic lifestyle. However, it's important to adjust your workout routine during the initial adaptation period, as your body adjusts to using fat as fuel. Some individuals may experience a temporary decrease in performance during this time. Once fully adapted, many people report sustained energy levels during exercise on these diets.
5. Is it safe to follow a low-carb or ketogenic diet long-term?
The long-term safety of low-carb and ketogenic diets is still under investigation. While short-term studies have shown benefits, there is limited research on the potential risks and benefits of long-term adherence. It's important to monitor your health markers, consult with a healthcare professional, and consider periodic breaks or cyclical approaches to ensure a well-rounded and sustainable dietary pattern.

Comments
Post a Comment